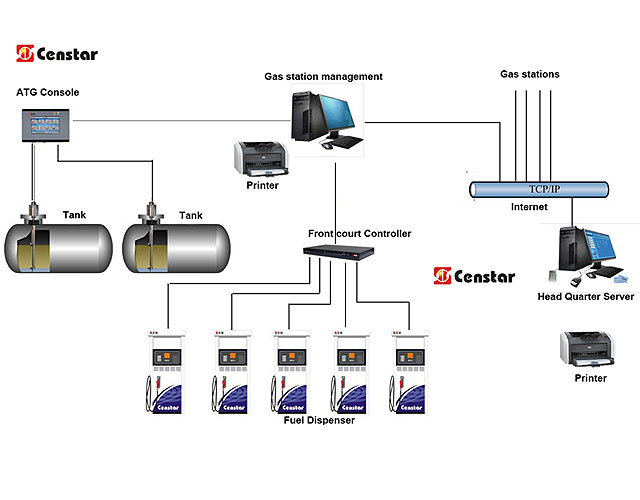
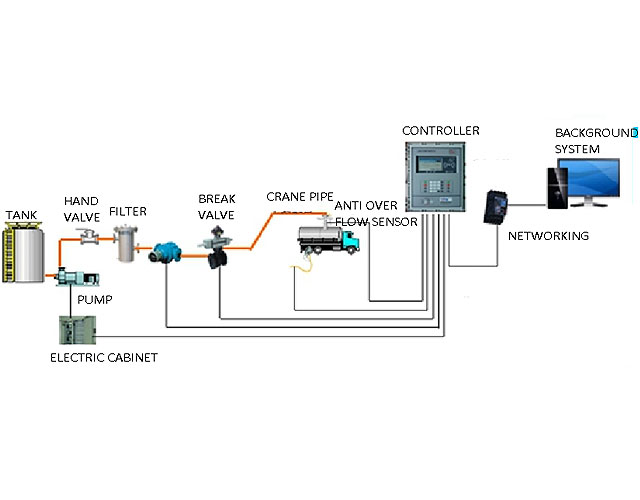
allowed co2 emissions from natural gas stations

Natural Gas Really Is Better Than Coal Science Smithsonian
Burning natural gas, for instance, produces nearly half as much carbon dioxide per unit of energy compared with coal. Natural gas is thus considered by many to be a “bridge fuel” that can help nations lower carbon emissions while they transition more slowly from

1.4 Natural Gas Combustion US EPA
CO2, CH4, and N2O emissions are all produced during natural gas combustion. In properly tuned boilers, nearly all of the fuel carbon (99.9 percent) in natural gas is converted to CO2 during the combustion process. This conversion is relatively independent of boiler or combustor type. Fuel carbon

GHG Emissions ConocoPhillips
Reducing emissions, even the small equipment leaks known as fugitive emissions, is a key aspect of our Global Onshore Well Management Principles. While there are differing methods and many measurement points, estimates of natural gas leakage rates between gas processing plants and electric power plants vary widely, from 0.7 to 2.6%.

How much carbon emissions does natural gas produce?
Industry and power stations are responsible for 50% of the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas) which releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.

Greenhouse Gases Equivalencies Calculator Calculations
Therms and Mcf of natural gas. Carbon dioxide emissions per therm are determined by converting million British thermal units (mmbtu) to therms, then multiplying the carbon coefficient times the fraction oxidized times the ratio of the molecular weight of carbon dioxide

Characterising the distribution of methane and carbon
However, whilst CO2 emissions from combustion are lower than those from coal or oil, emissions of CO2 and methane across the gas supply chain have been shown to be significant and vary widely, often by several orders of magnitude (Balcombe et al., 2017).

Fossil fuel power station Wikipedia
Fossil fueled power stations are major emitters of carbon dioxide (CO 2), a greenhouse gas which is a major contributor to global warming. The results of a recent study [3] show that the net income available to shareholders of large companies could see a significant reduction from the greenhouse gas emissions liability related to only natural

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Calculator Natural Gas Playbook
Engine emission data is sourced from model year 2016 diesel and natural gas engines certification data. CO2 and CH4 FEL (family emissions level) emissions over certification test cycles are used to calculate the fuel consumption, fuel economy, and test cycle thermal efficiency for model year 2016 natural gas vs model year 2016 diesel.

5 Natural Gas Vehicles: Impacts and Regulatory Framework
It then discusses the technology and infrastructure that will be needed for NG fueled trucks, which can operate on either compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG). It describes the regulatory framework for greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (primarily carbon dioxide, or CO2) and fuel economy standards.

1.4 Natural Gas Combustion US EPA
Greenhouse Gases 6 9 CO2, CH4, and N2O emissions are all produced during natural gas combustion. In properly tuned boilers, nearly all of the fuel carbon (99.9 percent) in natural gas is converted to CO2 during the combustion process. This conversion is relatively independent of boiler or combustor type.

Global Energy & CO2 Status Report: CO2 emissions
Driven by economics and policies, coal to gas switching avoided almost 60 Mt of coal demand, with the transition to less carbon intensive natural gas helping avert 95 Mt of CO2 emissions. Without this coal to gas switch, the increase in emissions would have been more than 15% greater.

EPA finalizes new methane standards for oil and gas
Methane is the main component of natural gas, and it’s much more potent than carbon dioxide as a heat trapping greenhouse gas. The EPA says new scientific data shows methane emissions are much higher than previously thought and nearly one third of

Greenhouse gas emissions by Turkey Wikipedia
Whereas natural gas, being methane (CH4), has 4 hydrogen atoms to burn for each one of carbon, and thus a medium CO2 emission intensity. Moreover, coal analyis of Turkish lignite, shows it to have a lot of ash [ citation needed ] and moisture, and to have a lower energy value of

How are carbon dioxide emissions affecting the Earth's
Total carbon dioxide emissions from human activities (burning fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas) and land use), 29 billion tonnes per year (2007 figures).

Specific Carbon Dioxide Emissions of Various Fuels
Burning of lignite emits nearly 100 % more carbon dioxide with respect to the energy content than burning of natural gas. Even natural fuels such as wood or peat have high specific emissions, if they are not used sustainable. Hence, deforestation has a high impact on climate change.
Why natural gas makes global warming worse GreenBiz
Here's the trouble: Carbon dioxide is the main greenhouse gas, but it's not the only one. Another one — present in smaller amounts, but far more potent — is CH4, otherwise known as methane, the primary component of natural gas. If you burn natural gas, you get less carbon dioxide than with coal.

Natural gas, the green choice? Resilience
However, natural gas (CH 4) itself is a potent greenhouse gas, and its release to the atmosphere without being burnt can quickly compensate for the CO 2 advantage against coal. On the left, CO2 emissions per kWh for coal and natural gas. On the right, the global warming potential of leaked CH4 expressed as

2017 UK GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS, PROVISIONAL
Carbon dioxide emissions from gas as a proportion of all carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels has increased from 25 per cent in 1990 to 50 per cent in 2017, whilst emissions from coal as a proportion of all fossil fuel carbon dioxide emissions has decreased from 38 per cent to 7 per cent over the same period.

Most Of The Rise In CO2 Likely Comes From Natural Sources
Yes, nature can cause global warming, but only in the course of millions of years because nature overall only produces approximately .6% of CO2 gases in a year, whereas the CO2 emissions are more than 3 4% every year around the world from industrial plants. China is a superb example that the rise in CO2 emissions is man made.

Comparing Emissions and Efficiency in Electric Cars and
Burning natural gas emits 117 pounds of carbon dioxide (CO2) per million BTUs and burning gasoline emits 157 pounds per million BTUs. Natural gas emits about 117/157 or about 75% of the CO2 of gasoline. Emissions Per Unit of Energy Consumed

How do human CO2 emissions compare to natural CO2 emissions?
Therefore human emissions upset the natural balance, rising CO2 to levels not seen in at least 800,000 years. In fact, human emit 26 gigatonnes of CO2 per year while CO2 in the atmosphere is rising by only 15 gigatonnes per year much of human CO2 emissions is being absorbed by natural sinks.

Modelling emissions from natural gas flaring ScienceDirect
On the average, anticipated gaseous emissions from natural gas of global origins with an average annual global flaring rate of 126 bcm per year (between 2000 and 2011), CO2 and CO emitted in million metric tonne (mmt) from flaring are 560 mmt and 48 mmt per annum.

Replacing Coal with Gas Is the Only Way to Catch Up in
Replacing coal with shale gas has allowed the U.S. to reduce CO2 emissions more than anyone else and for the world to catch up more of this must be done. Renewables such as solar and wind have achieved no significant dent in the energy production either.

Environmental Impacts of Natural Gas Union of Concerned
Natural gas emits 50 to 60 percent less carbon dioxide (CO2) when combusted in a new, efficient natural gas power plant compared with emissions from a typical new coal plant . Considering only tailpipe emissions, natural gas also emits 15 to 20 percent less heat trapping gases than gasoline when burned in today’s typical vehicle .

Coal vs. Natural Gas Energy Production
Global Energy Demand Is Growing! • Global energy demand grew by 8% from 2008 2012 • Demand projected to increase by 37% by 2040 • Development of renewables is being outpaced by

Assessment of Heavy Duty Natural Gas Vehicle Emissions
e per million Btu), according to the greet model natural gas emits 4 to 5 percent lower levels of ghg emissions than diesel throughout the fuel life cycle under a 100 year gWP time horizon and 19 to 24 percent higher levels of ghg emissions than diesel under a 20 year time horizon.

Greenhouse Gas Emissions per kWh for Site Fuels
Green house gas emissions data from burning fossil fuels, like natural gas or heating oil is relatively easy to come but can be confusing. To get the full picture you cannot just report CO2 emissions, since other greenhouse gasses are emitted as fuels are burned or electricity generated.

Dangerous Neighbors: Pipelines, Compressor Stations, and
Dangerous Neighbors: Pipelines, Compressor Stations, and Environmental Injustice Introduction: As natural gas continues to be touted as the transition fuel of choice, the industry’s extraction and rush to build infrastructure and its consequences have been coming under increased scrutiny. Natural gas

How much carbon dioxide is produced per kilowatthour of U
U.S. Electric Power Industry Estimated Emissions by State includes estimates for CO2 emissions by type of energy source in metric tons. You can convert metric tons to short tons by multiplying the number of metric tons by 1.1.

Main sources of carbon dioxide emissions What's Your Impact
There are both natural and human sources of carbon dioxide emissions. Natural sources include decomposition, ocean release and respiration. Human sources come from activities like cement production, deforestation as well as the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas.

How much carbon dioxide is produced when different fuels
Natural gas 117.0 The amount of CO2 produced when a fuel is burned is a function of the carbon content of the fuel. The heat content, or the amount of energy produced when a fuel is burned, is mainly determined by the carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) content of the fuel.

Infographic: The Climate Risks of Natural Gas Union of
The Climate Risks of Natural Gas. Much of the additional needed electricity is projected to come from natural gas, creating more emissions in the process. a primary component of natural gas leaks from drilling sites and pipelines. It is 34 times more potent than carbon dioxide at trapping heat.

Natural Gas Fuel Cells: Technology, Advances, and
Natural Gas Fuel Cells: Technology, Advantages Natural gas can contain 70 99% methane which is around 25 times stronger a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide. 3 These emissions during natural gas production and processing are estimated to make up around 20% of total GHG emissions from natural gas (based on emissions from the

Trapping Carbon Dioxide: Carbon Capture Technology
The CO2 rises to the top for collection, and the amine drops to the bottom for reuse [source: Allen]. The excess hydrogen also can be used for other energy production processes. Precombustion carbon capture is already in use for natural gas, and provides a much higher concentration of CO2

Infographic: The Climate Risks of Natural Gas Union of
The Climate Risks of Natural Gas. It is 34 times more potent than carbon dioxide at trapping heat. An estimated one to nine percent of all natural gas produced escapes into the atmosphere, equivalent to the global warming emissions from 35 314 typical sized coal power plants (600 megawatts).

Oil and Natural Gas Production, Processing, and Storage
The Greenhouse Gas Emission Standards for Crude Oil and Natural Gas Facilities is designed to reduce methane emissions from oil and gas production, processing, storage, and transmission compressor stations, which accounts for four percent of methane emissions in California. Regulated entities are required to take actions to limit intentional and unintentional emissions from equipment and

3.2 Natural Gas fired Reciprocating Engines
lubricating oil and from products of incomplete combustion. Emission of PM from natural gas fired reciprocating engines are generally minimal and comprise fine filterable and condensible PM. Increased PM emissions may result from poor air to fuel mixing or maintenance problems. 3.2.3.4 Carbon Dioxide, Methane, and Nitrous Oxide5 Carbon dioxide (CO

APPEA How natural gas can minimise greenhouse emissions
How natural gas can minimise greenhouse emissions Australia’s natural gas reserves have the unique potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions at low cost. This could occur both within Australia through the greater use of natural gas (particularly for electricity generation), and throughout the Asia Pacific region by increasing

U.S. Per Capita Carbon Emissions at Lowest Levels Since
Overall U.S. carbon emissions are at their lowest levels since 1992 and have declined 13 percent since 2005. The EIA has credited two thirds of the energy related carbon reductions achieved since 2005 to natural gas, which has prevented over two billion metric tons of carbon dioxide

Global Man made CO2 emissions 1965 2018: BP data Watts
The only applicable metric is the incremental GDP per ton of CO2 emissions as this is a measure of economic energy efficiency since CO2 emissions are roughly proportional to energy consumption. Minimizing CO2 is the wrong goal and it should be

Switch to Natural Gas Won't Reduce Carbon Emissions Much
In some scenarios, they found that use of natural gas would actually boost emissions from the power sector by up to 5 percent.

Natural gas is the most climate friendly fossil fuel in
natural gas produces kg of CO2 per kWh of electricity generated hard coal produces kg of CO2 per kWh of electricity generated The CO2 emissions for the average electricity production of all power stations in Germany With the average energy mix in Germany, kilograms of CO2 are currently produced for each

Oil and Natural Gas Production, Processing, and Storage
The Greenhouse Gas Emission Standards for Crude Oil and Natural Gas Facilities is designed to reduce methane emissions from oil and gas production, processing, storage, and transmission compressor stations, which accounts for four percent of methane emissions in California.

Pros and cons: Promise, pitfalls of natural gas » Yale
Pros and cons: Promise, pitfalls of natural gas By Bruce Lieberman on In the search to find cleaner alternatives to oil and coal in the climate change debate, America's rich supply of natural gas demands attention.